Introduction to Programming in C++
Welcome to the world of programming! Are you ready to start an exciting journey into the world of programming? Don’t worry if it sounds a bit scary - we’re here to make it super easy and fun for you!
What’s This Guide All About?
This guide is like your friendly neighbor who’s really good at puzzles. We’re going to help you learn how to solve computer puzzles (that’s what programming is!) using a language called C++. But we’re not just going to teach you random stuff - we’re focusing on something really cool called Data Structures and Algorithms. Don’t worry if those words sound big right now - by the end of this guide, you’ll be using them like a pro!
1. Introduction to Programming
Imagine you’re teaching your pet dog a new trick. You give it step-by-step instructions: “Sit”, “Roll over”, “Stand up”. That’s exactly what programming is! You’re giving your computer step-by-step instructions to do something cool.
C++ is just one of the many languages we can use to give these instructions. It’s like learning French or Spanish, but for talking to computers!
2. How to Approach Problems
When you’re faced with a tricky problem, it’s easy to feel lost. But don’t worry! We’ve got a super simple method to tackle any problem. It’s like a recipe for problem-solving:
Step 1:Understand the problem Just like reading a recipe before cooking, read the problem carefully. Make sure you know what it’s asking.Step 2:Enter appropriate input value for the problem This is like gathering all your ingredients before cooking. What information do you need to solve this problem?Step 3:Create logics/algorithms to solve the problem Now, think about the steps to solve the problem. It’s like planning how you’ll mix your ingredients and in what order.Step 4:Dry run the logics/algorithms for different test cases Before you start coding, test your plan in your head or on paper. It’s like tasting your dish before serving it to make sure it’s good!Step 5:Write code for the problem Finally, write your solution in C++. This is like actually cooking your meal after all the planning.
3. What is Pseudocode?
Pseudocode is like a rough draft of your program. It’s written in simple English (or any language you’re comfortable with) and describes what your program will do, step by step. It’s not actual code, but it helps you organize your thoughts before you start coding.
For example, pseudocode for making a sandwich might look like this:
1. Get two slices of bread2. Spread butter on one side of each slice3. Put a slice of cheese on one piece of bread4. Put the other slice of bread on top, buttered side down5. Put the sandwich in a pan6. Cook until golden brown on both sides4. What is a Flowchart?
A flowchart is like a map of your program. It uses different shapes and arrows to show the steps your program will take. It’s a visual way to represent your algorithm.
Components of a Flowchart:
Start/Stop:This is an oval shape that shows where your program begins and ends.Process:This is a rectangle that represents a step in your program.Input/Output:This is a parallelogram that shows when your program is getting information or showing results.Decision:This is a diamond shape that represents a yes/no question in your program.Arrow:These show the order of the steps in your program.On-Page Connector:This is a small circle that connects different parts of your flowchart on the same page.Off-Page Connector:This is like the on-page connector, but it connects parts of your flowchart that are on different pages.
How to Draw a Flowchart for a Problem with Pseudocode
Step 1:Write pseudocode Start by writing out your algorithm in simple language.Step 2:Draw flowchart Turn each step of your pseudocode into a flowchart shape.Step 3:Write code Use your flowchart as a guide to write your actual C++ code.
Practice with Flowchart, Pseudocode, and Code for Different Problems
Let’s practice with some simple problems. We’ll show you the pseudocode, flowchart, and C++ code for each one.
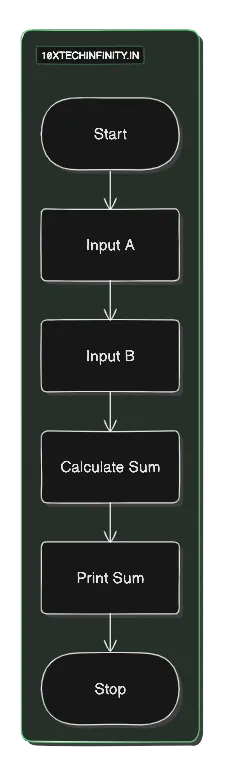
Problem 1: Print sum of A and B
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input number A3. Input number B4. Calculate Sum = A + B5. Print Sum6. StopFlowchart:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int A, B, Sum; cout << "Enter number A: "; cin >> A; cout << "Enter number B: "; cin >> B; Sum = A + B; cout << "Sum is: " << Sum; return 0;}Output:
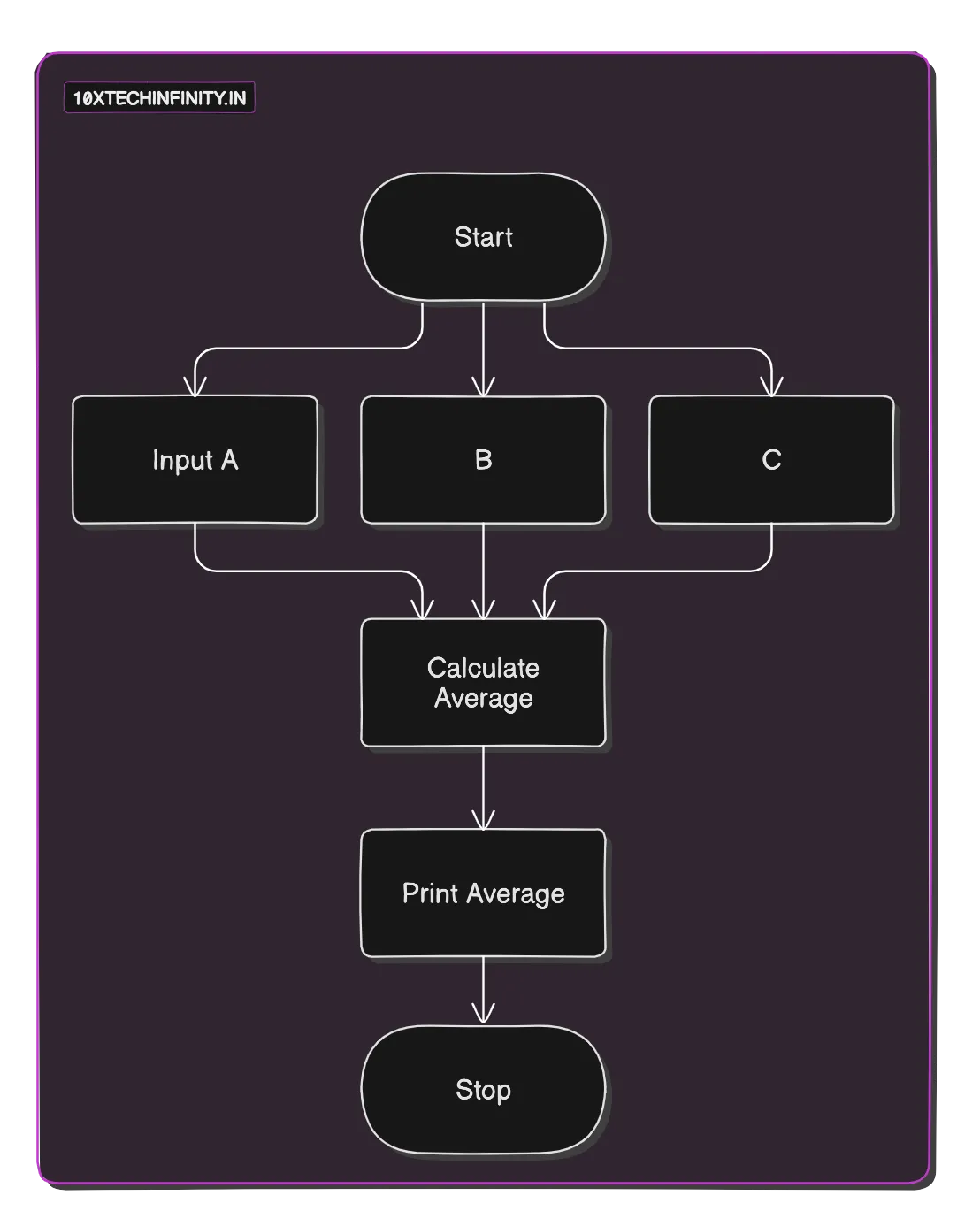
Enter number A: 10Enter number B: 20Sum is: 30Problem 2: Average of A, B, and C
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input numbers A, B, and C3. Calculate Average = (A + B + C) / 34. Print Average5. StopFlowchart:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { float A, B, C, Average; cout << "Enter three numbers: "; cin >> A >> B >> C; Average = (A + B + C) / 3; cout << "Average is: " << Average; return 0;}Output:
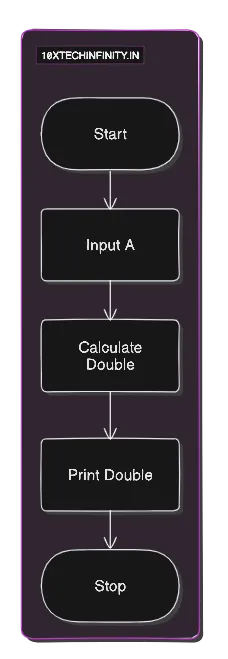
Enter three numbers: 10 20 30Average is: 20Problem 3: Print twice of A
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input number A3. Calculate Double = A * 24. Print Double5. StopFlowchart:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int A, Double; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> A; Double = A * 2; cout << "Twice of " << A << " is: " << Double; return 0;}Output:
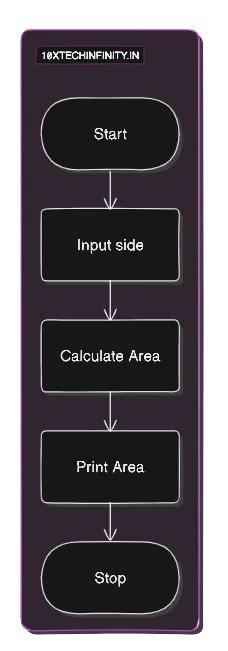
Enter a number: 10Twice of 10 is: 20Problem 4: Find area of square
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input side length of square3. Calculate Area = side * side4. Print Area5. StopFlowchart:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { float side, area; cout << "Enter the side length of the square: "; cin >> side; area = side * side; cout << "Area of the square is: " << area; return 0;}Output:
Enter the side length of the square: 10Area of the square is: 100Problem 5: Calculate overall percentage from marks
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input marks for 5 subjects3. Calculate Total = sum of all marks4. Calculate Percentage = (Total / 500) * 1005. Print Percentage6. StopFlowchart:
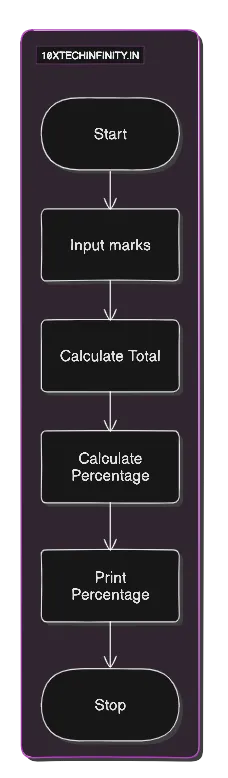
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { float marks[5], total = 0, percentage; cout << "Enter marks for 5 subjects: "; for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cin >> marks[i]; total += marks[i]; } percentage = (total / 500) * 100; cout << "Overall percentage: " << percentage << "%"; return 0;}Output:
Enter marks for 5 subjects: 90 80 70 60 50Overall percentage: 80.0%Problem 6: Check if number is even or odd
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input number3. If (number % 2 == 0) Print "Even" Else Print "Odd"4. StopFlowchart:
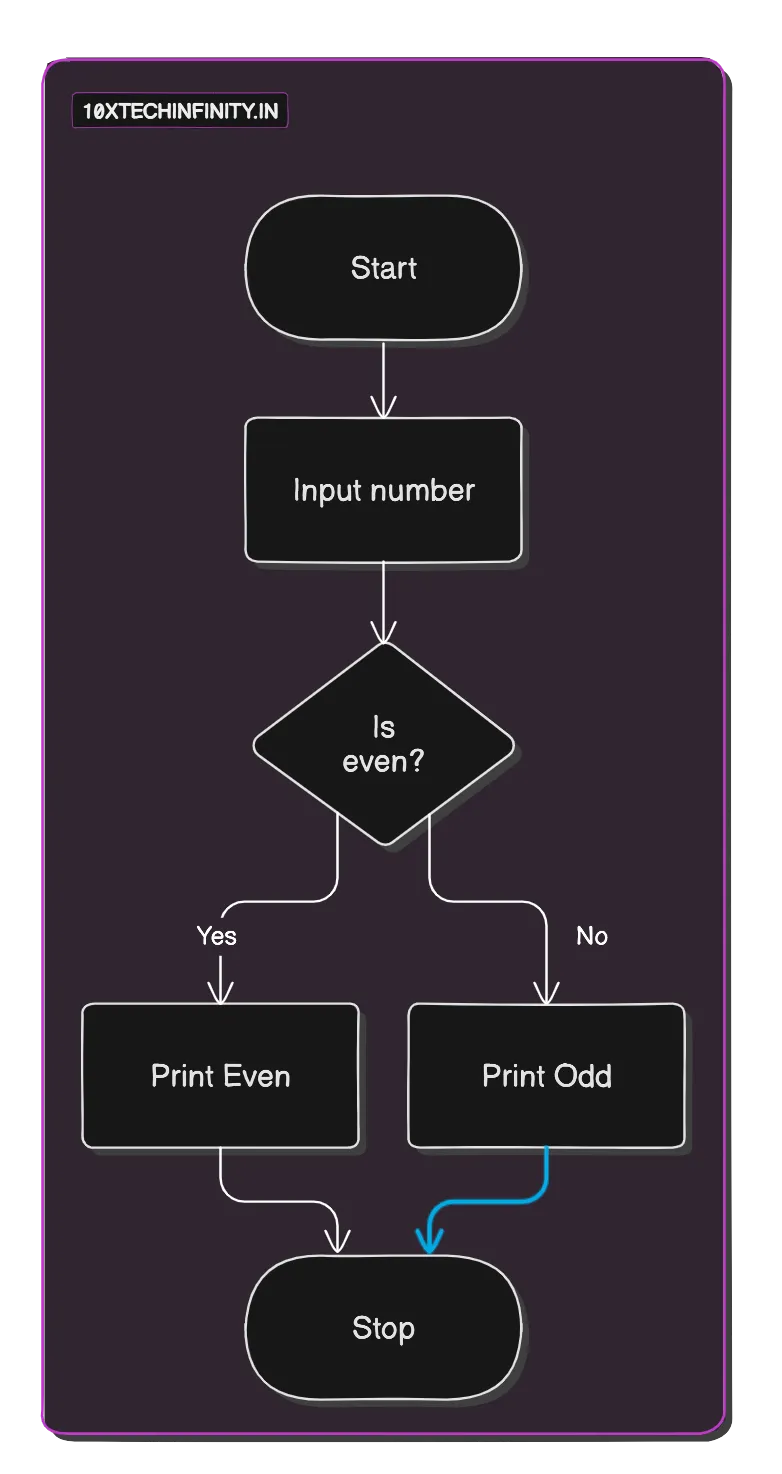
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int number; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> number; if(number % 2 == 0) cout << number << " is Even"; else cout << number << " is Odd"; return 0;}Output:
Enter a number: 1010 is EvenProblem 7: Check number is positive or negative or zero
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input number3. If (number > 0) Print "Positive" Else If (number < 0) Print "Negative" Else Print "Zero"4. StopFlowchart:
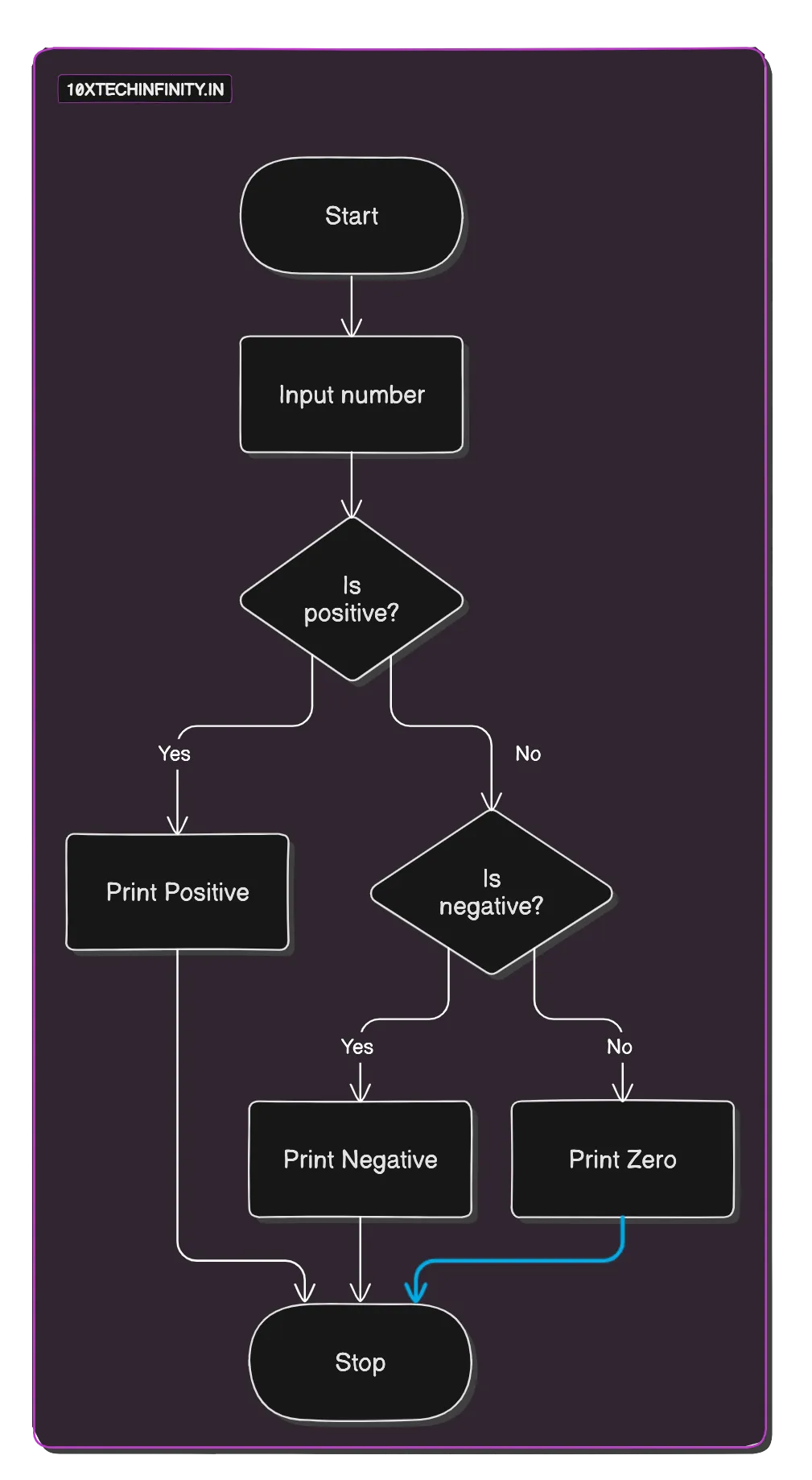
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int number; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> number; if(number > 0) cout << number << " is Positive"; else if(number < 0) cout << number << " is Negative"; else cout << "The number is Zero"; return 0;}Output:
Enter a number: 1010 is PositiveProblem 8: Create student and grade flowchart and pseudocode
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input student name3. Input marks for 3 subjects4. Calculate average = (subject1 + subject2 + subject3) / 35. If (average >= 90) Grade = 'A' Else If (average >= 80) Grade = 'B' Else If (average >= 70) Grade = 'C' Else If (average >= 60) Grade = 'D' Else Grade = 'F'6. Print student name, average, and grade7. StopFlowchart:
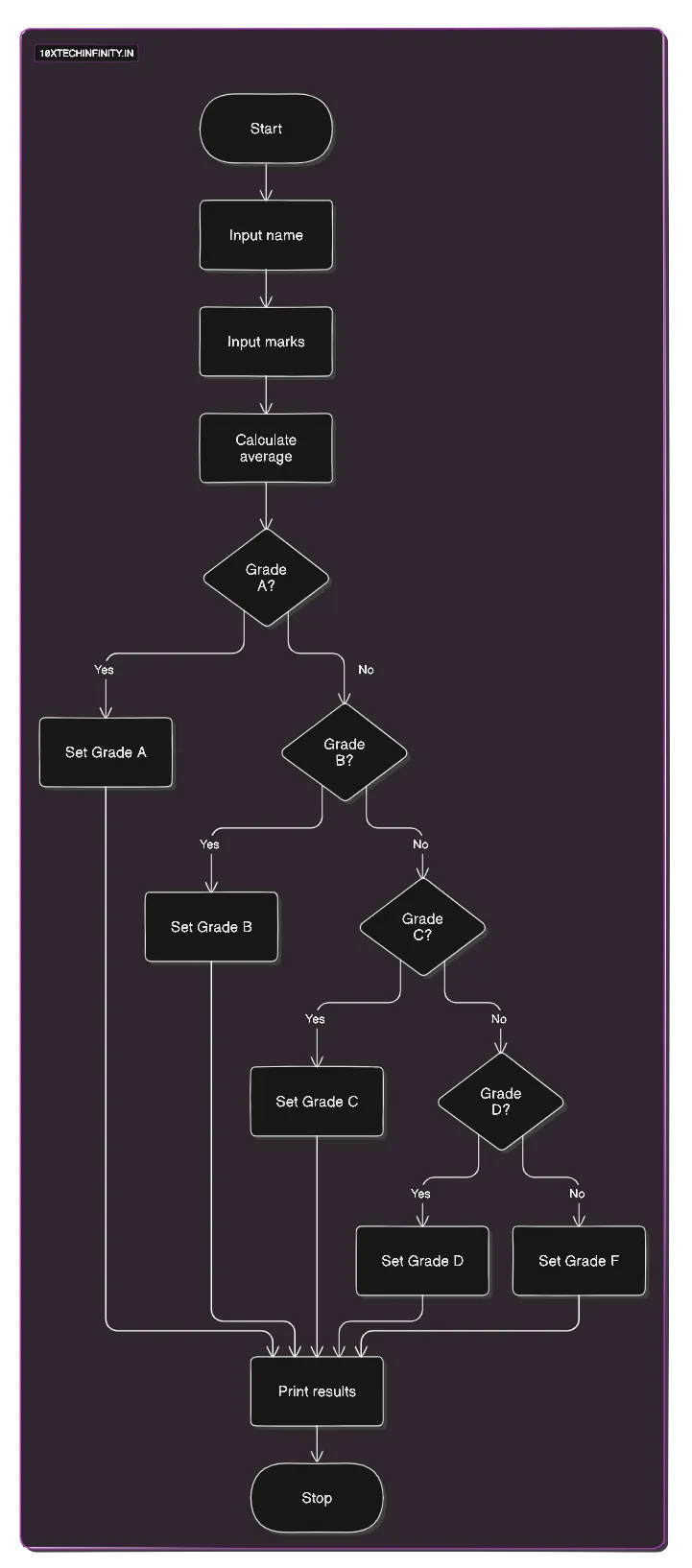
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>#include <string>using namespace std;
int main() { string name; float subject1, subject2, subject3, average; char grade;
cout << "Enter student name: "; getline(cin, name); cout << "Enter marks for 3 subjects: "; cin >> subject1 >> subject2 >> subject3;
average = (subject1 + subject2 + subject3) / 3;
if(average >= 90) grade = 'A'; else if(average >= 80) grade = 'B'; else if(average >= 70) grade = 'C'; else if(average >= 60) grade = 'D'; else grade = 'F';
cout << "Student: " << name << endl; cout << "Average: " << average << endl; cout << "Grade: " << grade;
return 0;}Output:
Enter student name: Manoj KumarEnter marks for 3 subjects: 80 90 70Student: Manoj KumarAverage: 80.0Grade: BProblem 9: Counting number from 1 to n
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input n3. Set counter = 14. While (counter <= n) Print counter Increment counter5. StopFlowchart:
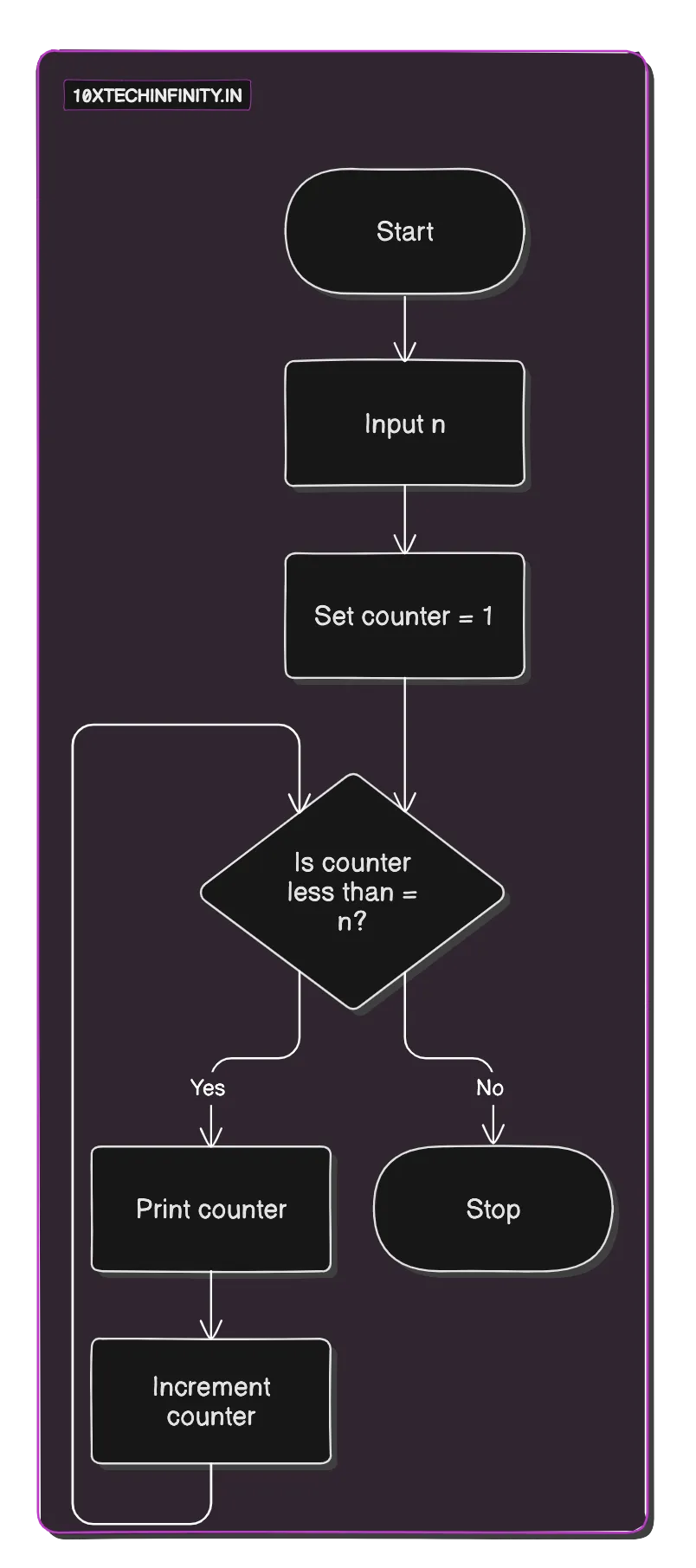
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int n, counter = 1; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> n; while(counter <= n) { cout << counter << " "; counter++; } return 0;}Output:
Enter a number: 101 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Problem 10: Multiplying number from 1 to n
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input n3. Set result = 14. For i = 1 to n result = result * i5. Print result6. StopFlowchart:
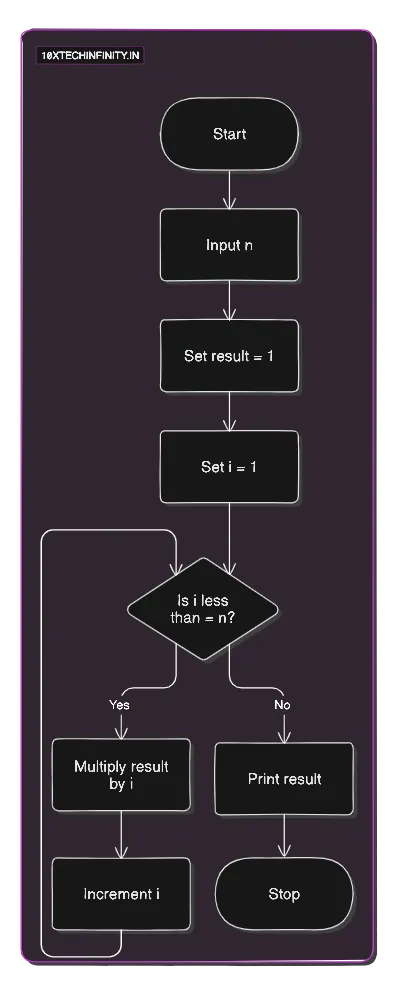
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int n, result = 1; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> n; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { result *= i; } cout << "Product of numbers from 1 to " << n << " is: " << result; return 0;}Output:
Enter a number: 5Product of numbers from 1 to 5 is: 120Problem 11: Print even numbers from 1 to n
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input n3. Set counter = 24. While (counter <= n) Print counter Increment counter by 25. StopFlowchart:
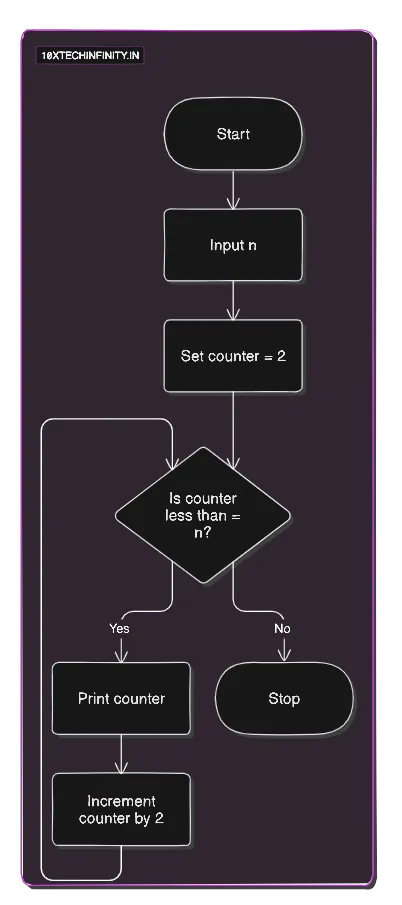
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int n, counter = 2; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> n; cout << "Even numbers from 1 to " << n << " are: "; while(counter <= n) { cout << counter << " "; counter += 2; } return 0;}Output:
Enter a number: 10Even numbers from 1 to 10 are: 2 4 6 8 10Problem 12: Multiplying two numbers A and B taking input from user
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input number A3. Input number B4. Calculate Product = A * B5. Print Product6. StopFlowchart:
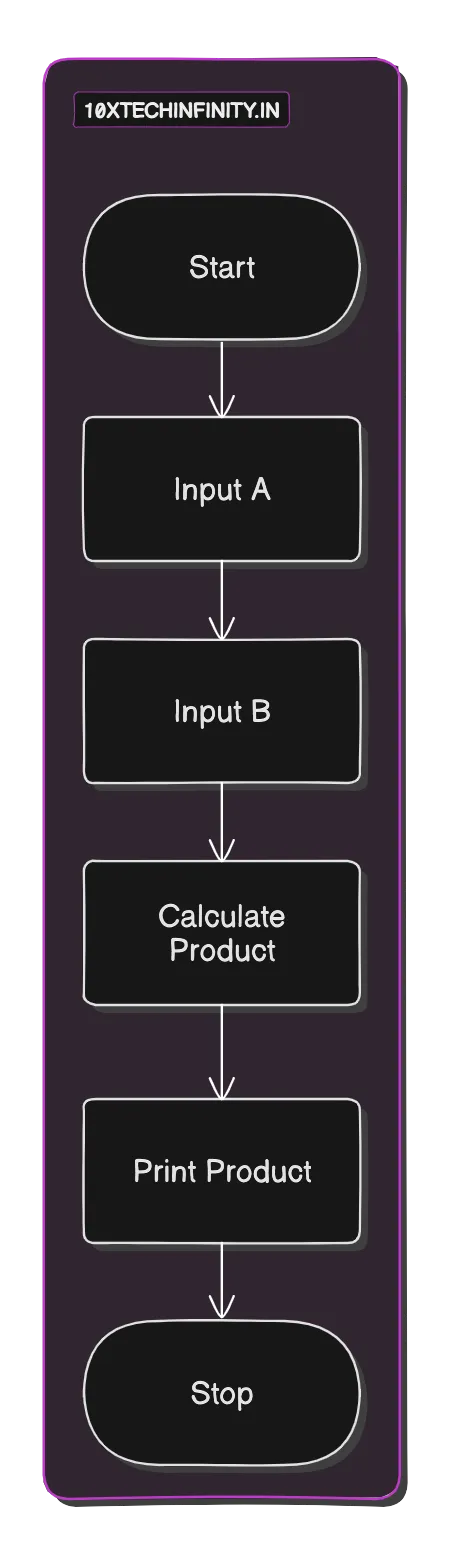
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int A, B, Product; cout << "Enter number A: "; cin >> A; cout << "Enter number B: "; cin >> B; Product = A * B; cout << "Product of " << A << " and " << B << " is: " << Product; return 0;}Output:
Enter number A: 5Enter number B: 10Product of 5 and 10 is: 50Problem 13: Find the perimeter of triangle
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input side1, side2, side33. Calculate Perimeter = side1 + side2 + side34. Print Perimeter5. StopFlowchart:
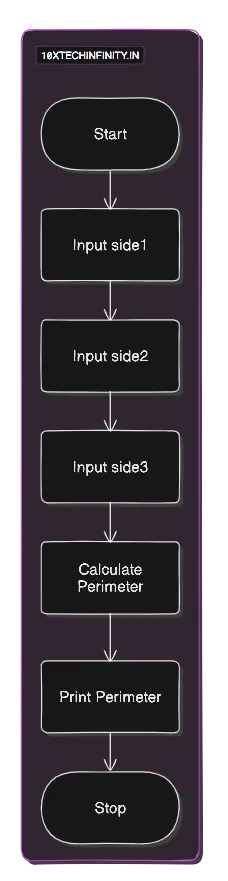
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { float side1, side2, side3, perimeter; cout << "Enter the lengths of three sides of the triangle: "; cin >> side1 >> side2 >> side3; perimeter = side1 + side2 + side3; cout << "The perimeter of the triangle is: " << perimeter; return 0;}Output:
Enter the lengths of three sides of the triangle: 5 6 7The perimeter of the triangle is: 20Problem 14: Find the simple interest
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input Principal (P), Rate (R), Time (T)3. Calculate SimpleInterest = (P * R * T) / 1004. Print SimpleInterest5. StopFlowchart:
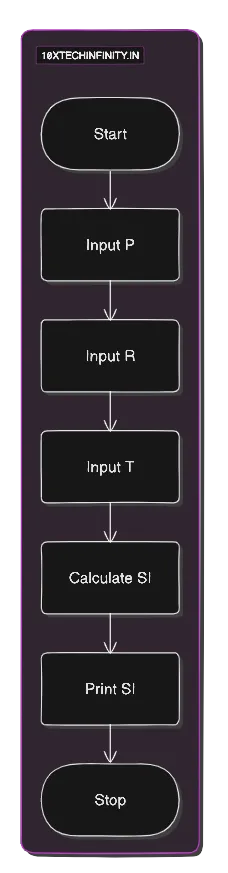
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { float principal, rate, time, simpleInterest; cout << "Enter Principal amount: "; cin >> principal; cout << "Enter Rate of interest (per year): "; cin >> rate; cout << "Enter Time (in years): "; cin >> time; simpleInterest = (principal * rate * time) / 100; cout << "Simple Interest is: " << simpleInterest; return 0;}Output:
Enter Principal amount: 1000Enter Rate of interest (per year): 10Enter Time (in years): 2Simple Interest is: 200Problem 15: Find the compound interest
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input Principal (P), Rate (R), Time (T), Number of times interest is compounded per year (n)3. Calculate Amount = P * (1 + R/(100*n))^(n*T)4. Calculate CompoundInterest = Amount - P5. Print CompoundInterest6. StopFlowchart:
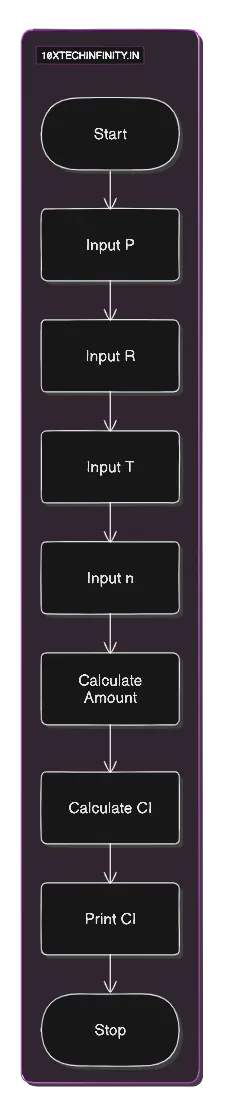
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;
int main() { float principal, rate, time, n, amount, compoundInterest; cout << "Enter Principal amount: "; cin >> principal; cout << "Enter Rate of interest (per year): "; cin >> rate; cout << "Enter Time (in years): "; cin >> time; cout << "Enter number of times interest is compounded per year: "; cin >> n; amount = principal * pow((1 + rate/(100*n)), (n*time)); compoundInterest = amount - principal; cout << "Compound Interest is: " << compoundInterest; return 0;}Output:
Enter Principal amount: 1000Enter Rate of interest (per year): 10Enter Time (in years): 2Enter number of times interest is compounded per year: 2Compound Interest is: 200Problem 16: Print counting from n to 1
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input n3. While (n >= 1) Print n Decrement n4. StopFlowchart:
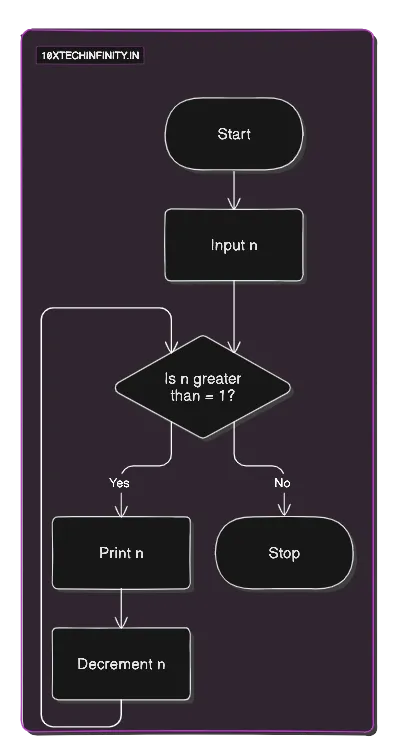
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int n; cout << "Enter a number: "; cin >> n; cout << "Counting from " << n << " to 1: "; while(n >= 1) { cout << n << " "; n--; } return 0;}Output:
Enter a number: 5Counting from 5 to 1: 5 4 3 2 1Problem 17: Find the factorial of a number
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input n3. Set factorial = 14. For i = 1 to n factorial = factorial * i5. Print factorial6. StopFlowchart:
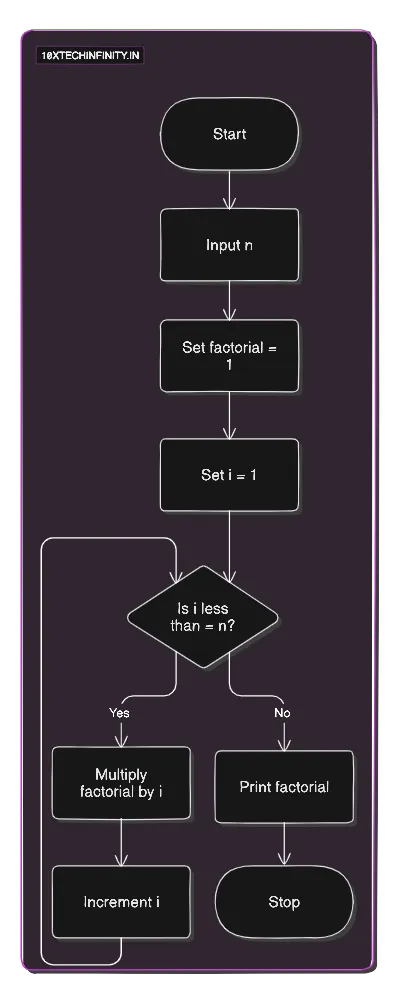
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int n; unsigned long long factorial = 1; cout << "Enter a positive integer: "; cin >> n; if (n < 0) cout << "Error! Factorial of a negative number doesn't exist."; else { for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { factorial *= i; } cout << "Factorial of " << n << " = " << factorial; } return 0;}Output:
Enter a positive integer: 5Factorial of 5 = 120Problem 18: Check if number is prime or not
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input n3. If n <= 1 Print "Not Prime"4. For i = 2 to sqrt(n) If n is divisible by i Print "Not Prime" Stop5. Print "Prime"6. StopFlowchart:
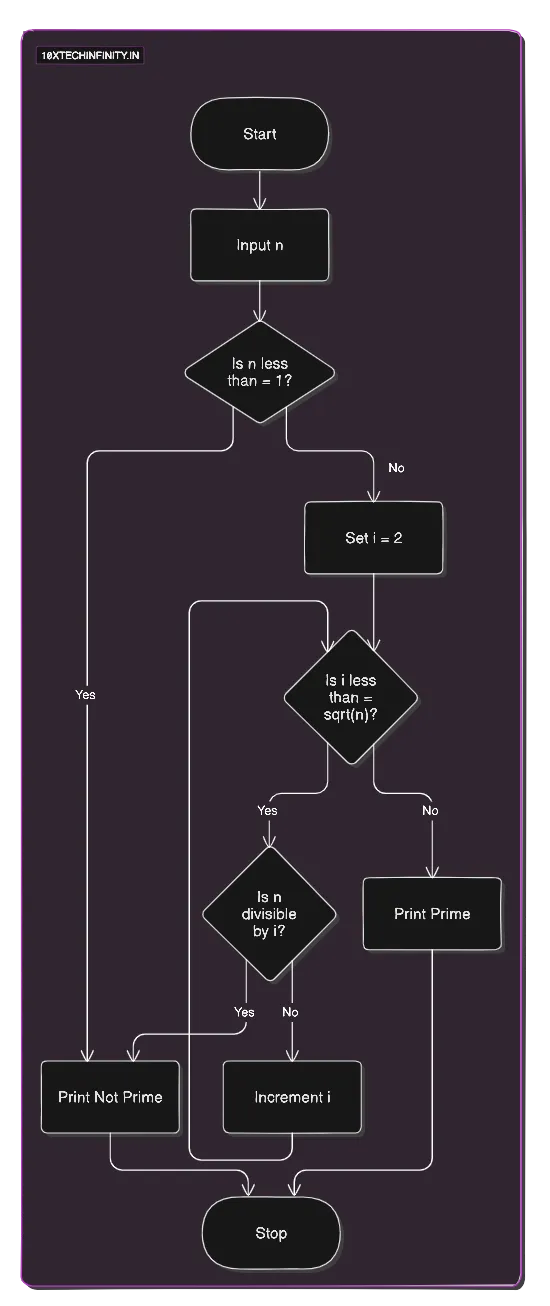
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>#include <cmath>using namespace std;
int main() { int n; bool isPrime = true; cout << "Enter a positive integer: "; cin >> n; if (n <= 1) { isPrime = false; } else { for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); ++i) { if (n % i == 0) { isPrime = false; break; } } } if (isPrime) cout << n << " is a prime number"; else cout << n << " is not a prime number"; return 0;}Output:
Enter a positive integer: 55 is a prime numberProblem 19: Check valid triangle or not
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input side1, side2, side33. If (side1 + side2 > side3) AND (side2 + side3 > side1) AND (side3 + side1 > side2) Print "Valid Triangle" Else Print "Not a Valid Triangle"4. StopFlowchart:
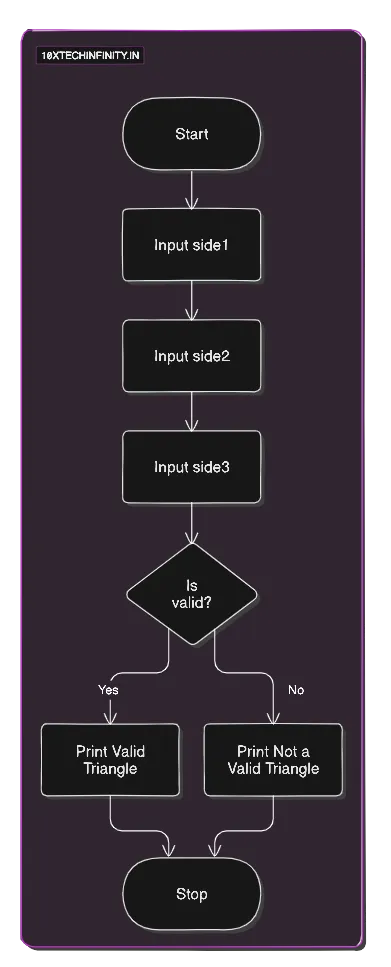
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { float side1, side2, side3; cout << "Enter the lengths of three sides of the triangle: "; cin >> side1 >> side2 >> side3; if (side1 + side2 > side3 && side2 + side3 > side1 && side3 + side1 > side2) cout << "This is a valid triangle"; else cout << "This is not a valid triangle"; return 0;}Output:
Enter the lengths of three sides of the triangle: 3 4 5This is a valid triangleProblem 20: Print the maximum number from three numbers A, B, and C
Pseudocode:
1. Start2. Input A, B, C3. Set max = A4. If B > max max = B5. If C > max max = C6. Print max7. StopFlowchart:
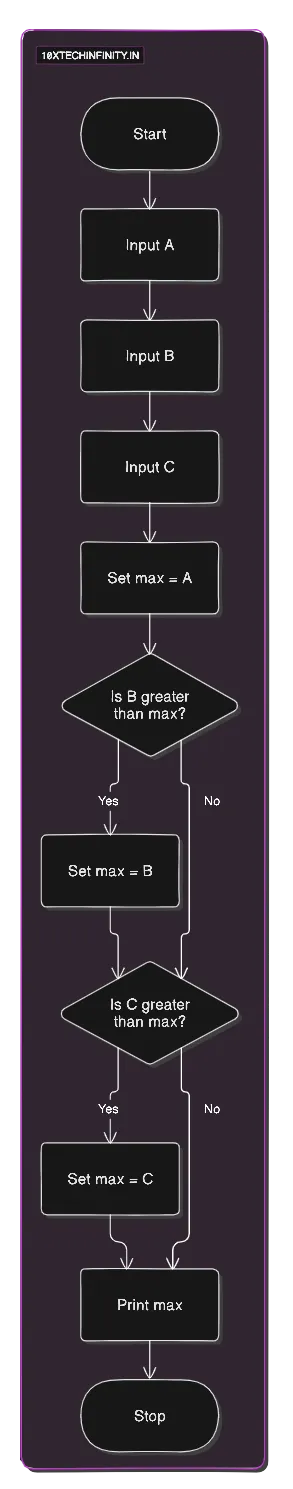
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
int main() { int A, B, C, max; cout << "Enter three numbers: "; cin >> A >> B >> C; max = A; if(B > max) max = B; if(C > max) max = C; cout << "The maximum number is: " << max; return 0;}Output:
Enter three numbers: 3 4 5The maximum number is: 5Conclusion
This guide covers the basics of programming in C++ with a focus on problem-solving techniques. It includes an introduction to programming, problem-solving approaches, pseudocode, flowcharts, and practical examples with code. The content is presented in an easy-to-understand manner, suitable for beginners in programming.
Happy coding!
